Uveal Melanoma
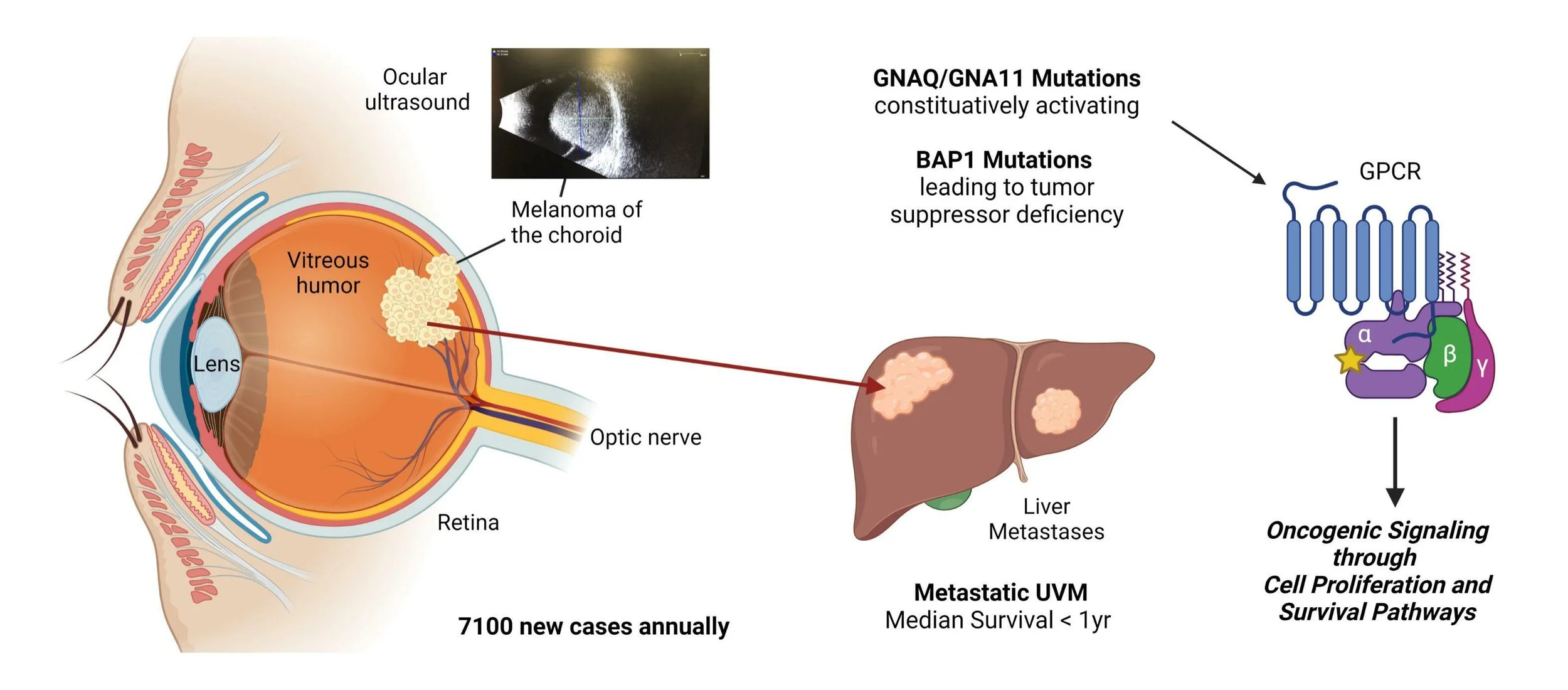
Uveal melanoma is a rare disease that occurs mainly in patients of European ancestry. Tumors can occur in the iris or ciliary body, but the most commonly location is in the choroid. Somatic or germline mutation of the BAP1 (BRCA1-associated protein 1) tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 3p21.1 predisposes patients to develop uveal melanoma. Somatic mutations in the alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins (GNAQ, GNA11) which couple seven-transmembrane domain receptors to cell proliferation and survival pathways, cause the G signaling protein to become locked in a constituently active state and drive uncontrolled tumor growth. Currently, first line treatments for the primary tumor are resection, radiation therapy and enucleation. After the primary site has been treated, long term survival depends critically on the high risk for metastatic disease to the liver. Median survival for metastatic uveal melanoma is less than one year.